Starting the Server
Linux Distributions (Linux apt/yum Installer)
Running the EMS after installation is as simple as starting the EMS service:
# service evostreamms start
# service evostreamms stop
# service evostreamms restart
The EMS can also be run in console mode:
# service evostreamms start_console
Linux, Mac OSX and BSD Distributions (.tar.gz Distribution)
There are two “run” scripts that can be used to start the EvoStream Media Server:
-
Run EMS with console logs, using
config/config.luaas the main server configuration.$ ./run_console_ems.sh -
Run EMS as a background process. The script will attempt to assign the run-process to the user
evostream.$ ./run_daemon_ems.sh
Notes:
- Either command can be directly executed.
- For
run_daemon_ems.sh, if theevostreamuser does not exist, an error will be printed to the screen. Despite the error, the EMS will probably have been started. To check if the server is running, user can issueps –ef | grep evostreamin terminal.
This command will print differently on different operating systems, but it should let you know that the server is running.
- The user used by
run_daemon_ems.shcan easily be modified by changing the value after the-uin the script itself. - The user running the EvoStream Media Server must have sufficient permission to open and bind to network ports.
Windows Distribution
The EMS may be started and stopped using the Windows Services tool in Windows.
User may directly run the EMS using the shortcut icon if added during installation, or the batch file for running the server in a command prompt:
C:\EvoStream\> run_console_ems.bat
This script simply runs the Media Server through the command prompt, using config/config.lua as the main server configuration. This file can also be double-clicked to start the server. The EvoStream Media Server icon on the desktop can also be double-clicked to do the same thing.
There are other scripts that can be used to create and manipulate the server as a Windows® Service. These scripts need to be run as an administrator. User can verify they have worked by opening the Windows Services tool and looking for the EMS service.
C:\EvoStream\services\ems\create.bat: Creates and starts the Windows serviceC:\EvoStream\services\ems\remove.bat: Removes the Windows serviceC:\EvoStream\services\ems\start.bat: Starts the service if it has not already been startedC:\EvoStream\services\ems\stop.bat: Stops the service if it is currently running
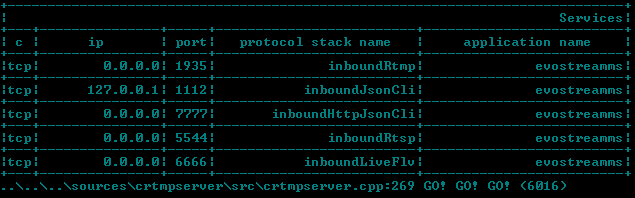
Startup Success
For either Windows or Linux/BSD/OSX, when you run the EMS as a console application, you should see the following screen indicating the server is up and running:
EMS Command Line Definition
The evostreamms executable can be run with a few different options. The command line signature is as follows:
Format: evostreamms [OPTIONS] [config_file_path]
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| –help | Prints this help and exit. |
| –version | Prints the version and exit. |
| –use-implicit-console-appender | Adds extra logging at runtime, but is only effective when the server is started as a console application. This is particularly useful when the server starts and stops immediately for an unknown reason. It will allow you users to see if something is wrong, particularly with the config file. |
| –daemon | Overrides the daemon setting inside the config file and forces the server to start in daemon mode. |
| –uid= |
Run the process with the specified user id. |
| –gid= |
Run the process with the specified group id. |
| –pid=<pid_file> | Create PID file. Works only if –daemon option is specified. |