Quick Start Guide for Microsoft Azure Load Balancer
Purpose
This document describes how to set up the EvoStream HTML5 Low-Latency Broadcast Template on Microsoft Azure.
This template will provide you with a flexible an scalable Origin-Edge distribution platform for low-latent HTML5 video streaming. An Azure Scale Set is used to scale your Edge Virtual Machines and an Azure Load Balancer handles the distribution of load accross the active Edge VM’s. An Origin Server is provided to source the streams.
A Stream Manager virtual machine is used to manage the distributions of streams between origin and edge.
For more information with Azure Load Balancer, see documentation here.
Getting Started
Pre-requisites
- Microsoft Account
- Working knowledge of Azure virtual machines
-
Working knowledge of OTT Video Streaming
Setup Virtual Machine Environment
To get started with the EvoStream Media Server (EMS) on Azure, the first thing to do is to setup the virtual machine by simply following these steps:
-
Search for the EvoStream Media Server in the Azure marketplace, or simply follow this link.
-
Click on GET IT NOW
-
Select the load balancer plan for the virtual machine to be created. Click on Continue.
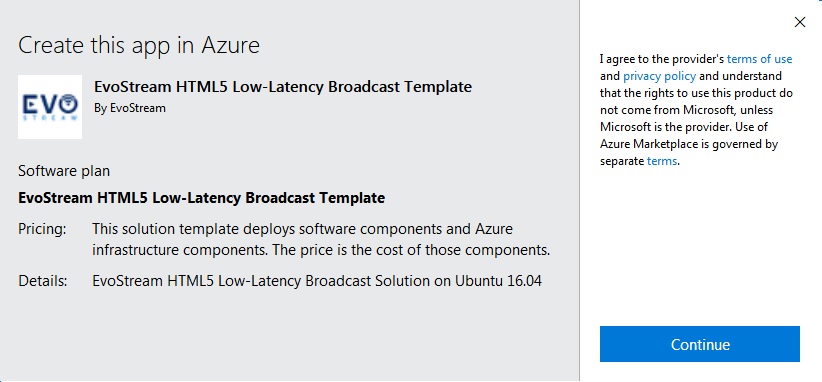
Image available:
-
EvoStream Media Server for Ubuntu - Ubuntu 16.04 64-bit
-
Configure the virtual machine settings based on your preferences:
A. Basics - configure basic settings
- Unique Suffix
- Username
- SSH public key ~Click here to know how to create a SSH public key.~
- Subscription
- Resource Group
- Location
B. VM Configuration - configure the VMs
- VM Size
- HTTP password
- Confirm password
-
Review the Settings, Offer Details and Terms of Use then click Purchase to start the deployment
-
To check if the image has been created, on the Microsoft Azure Dashboard, click on the Virtual machines. You will now see the image created once the deployment succeeded.
You should have these machines after creation:
1 Stream Manager
1 Origin
1 Edge (with two instances)
1 Load Balancer
Virtual Machine List in Resource Group Stream Manager, Origin, Edge Load Balancer 
Edge instances
Note: The machines are started after the deployment
EMS Machine Components
When creating a machine with load balancer, three machines are actualy created. These are all included in the EMS template. The machines functions as follows:
A. Stream Manager
-
Maintains a map of active Origin and Edges
-
Detects ingest events at Origin to trigger stream replication at Edges
- Pulls streams to Edges when Origin ingests new streams
- Updates configuration when VM creation event detected
- Updates configuration when Server Started event detected
- Pings Origin & Edges regularly to update configuration
B. Origin Server
-
Ingests streams from Source Clients
-
Requests SM to replicate ingested streams to Edges
-
Registers to NLM on VM creation
C. Edge Server
-
Replicate (pull) streams ingested by Origin
-
Register to NLM on VM creation
D. Load Balancer
- Distributes load among Edges
E. Auto-Scaler
- Automatically scales Edges based on bandwidth usage
Connecting to EMS machine
All the virtual machines in your account is seen under the Virtual machines in the left-side menu bar.
Note: All VMs are started after creation.
If your machine is turned off, manually start the set of VMs; SM, Origin, Edge in your resource group.
To start anything for your project, what you need to access is the Origin Server. An EMS is installed in this server. From here, you can pull your streams and the Stream Manager will do the replication of the streams to the Edge Servers. The Edge Servers will be accessed by clients when a request is sent for streaming.
A. Connecting via SSH from Linux Terminal
-
Send command:
ssh -1 <private_keyname> <username>@<OriginServer_IPaddress>Note: You should be in the path of the private key.
user@ubuntu:~/Desktop$ ssh -1 evostreamkey user@11.221.105.202 The authenticity of host '111.221.105.202 (111.221.105.202)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is 3c:1b:60:14:c0:5c:24:ab:9e:63:20:66:87:6c:12:b0. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes -
Input “yes”, press Enter
Warning: Permanently added '111.221.105.202' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-28-generic x86_64) Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/ Get cloud support with Ubuntu Advantage Cloud Guest: http://www.ubuntu.com/business/services/cloud 15 packages can be updated. 1 update is a security update. The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law. To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>". See "man sudo_root" for details. -
Check if EMS is running by sending
ps -e|grep evo1912 ? 00:00:00 evostreamms 1913 ? 00:00:00 evo-webserver
You are now connected to EMS!
Notes:
-
The license is already installed and is placed in
/etc/evostreamms. -
Number of EMS instance depends on the VM size.
B. Connecting via SSH using PuTTy
Pre-requisites:
- PuTTY Secure Shell Client
- PuTTY Generator
B.1. Key File Conversion
On Windows® operating systems, you can open a secure session to your Azure instance by using the PuTTY Secure Shell client, which you can download here.
The first thing you’ll need to do is convert the private key. The PuTTY Secure Shell client doesn’t natively support the private key format generated in the given link above.
PuTTY has a tool called PuTTYgen that you can use to convert your private key to the required PuTTY Private Key File (*.ppk) format. To convert the private key file that you created to a [key-pair-name].ppk file, do the following:
- Run PuTTY Key Generator
- Click Load button

-
Select and open the private key file that you want to convert in the Load private key window.
Note: You’ll need to select the All Files option in the File filter drop-down list to see private key files in the file list.
-
Click OK in the PuTTYgen Notice window
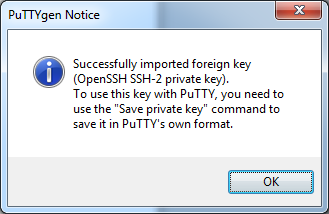
-
Click Save private key and save the file with the name [key-pair-name].ppk.
B.2. Connecting via SSH
-
Run PuTTY
-
Select Session under the category tree
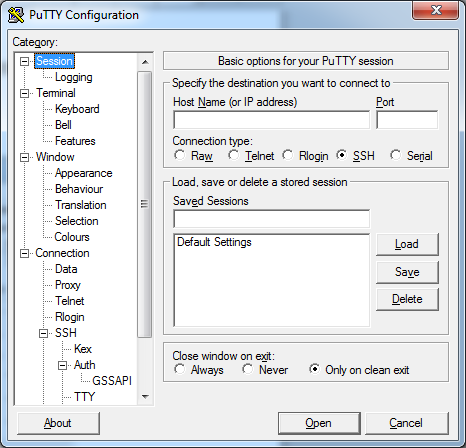
-
Specify the destination you want to connect to:
Host Name – the username and public IP address of the Origin Server
Port – 22 (default)
Connection type – SSH
-
Select Auth under Connection > SSH in category tree
-
Click the Browse button to find and open the [key-pair-name].ppk file
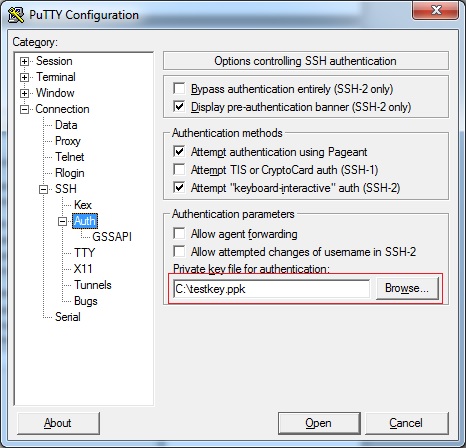
Note: If you will be opening this same session later, you can save it for future use
-
Click Open
-
Click Yes to accept the security key on the PuTTy Security Alert Window
-
You are now connected to the machine!
Note: The license is already installed and is placed in
/etc/evostreamms.
Load Balancing
Azure Load Balancer delivers high availability and network performance to EMS Edge servers. It distributes outbound traffic among healthy instances of Edge servers defined in a load-balanced scale set.

The Azure Load Balancer (or ALB) consists of an Ingest side, a Delivery side, and a Stream Manager.
The Ingest side consists of an Origin server (a Virtual Machine or VM with EMS). The Delivery side consists of a variable number of Edge servers (VMs with EMS) that are part of a Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS). The Scale Set is equipped with an Auto Scaler to increase or decrease the number of Edge VMs depending on the total outbound bandwidth. The Scale Set uses a Load Balancer to distribute the load among the Edge VMs. The Stream Manager (SM) coordinates all streaming activities at the Origin and Edge servers.
At the Ingest side, when a stream is ingested by the Origin server, the Stream Manager will be notified of a stream creation event. The SM will then ask each Edge server (each instance in the Scale Set) to pull the stream from the Origin server as an RTMP stream. At the Delivery side, when a client plays or pulls a stream, the Load Balancer randomly selects an available Edge server in the Scale Set to serve the requested stream to the client.
Scale In and Scale Out
As more clients consume streams, the outbound bandwidth reaches a threshold at which the Autoscaler will add a new instance (an Edge VM) to the Scale Set. This is called scaling out. There is a maximum number of instances in the Scale Set (currently 5). The maximum bandwidth capacity depends on the VM size of the Scale Set.
On the other hand, as fewer client consume streams, the outbound bandwidth drops below a threshold at which the Auto Scaler will delete an instance (an Edge VM) from the Scale Set. This is called scaling in. There is a minimum number of instances in the Scale Set (currently 2).
Pushing Stream to Origin
First things first after VM deployment is to push a stream or streams into your Origin machine. You can push a stream using other EMS or other third party media players.
To check on the Origin machine’s IP address, go to your resource group > check for the origin virtual machine > click on Overview. You can find the public IP address in this page.
Pushing stream using EMS
If you wished to push a stream to your origin machine using EMS, you need to know the destination address and localstreamname of the source to be pushed then send this command:
pushStream uri=rtmp://Origin_IPAddress/live localStreamname=<localStreamname> targetStreamName=<targetStreamName>
You may check if the stream if successfully pushed to the Origin server here.
Just enter the Origin’s IP address and the localStreamName of the stream and hit Play.
To know more about pushStream API, click here.
Terminating EMS machine
Stopping EMS machine
When you want to stop the virtual machine, fret not, all the changes remains in the server. The machine is only in suspended.
- Click on the Virtual Machine Server menu
- Right click on the virtual machine name, click on Stop
- or, simply click Stop on the virtual machine window
-
Confirm stopping the virtual machine by clicking Yes
Notes:
- There is no Stop function for Edge Server and its instances.
- If the machine is stopped, the IP address of the machine will change on start.
Deleting EMS machine
Deleting the EMS virtual machine will remove all the changes and the virtual machine itself in the Azure Virtual Machine list.
- Click on the Virtual machine menu
- Right click on the virtual machine name, click on Delete
- or, simply click Delete on the virtual machine window
-
Choose if you want to delete or keep the attached disk
Notes:
-
For Edge, you need to stop the instances. Just go under the Instances menu and you will find all the running instances in your Edge Server.
-
Another edge instance will be created when one is deleted. For the two initial edge only.